Probability Calculator
Calculate probabilities for statistical analysis and decision making
Probability Calculator
Probability is the measure of the likelihood of an event occurring. Calculate probabilities for various scenarios including two independent events, normal distribution, and series of events with our comprehensive probability calculator.
Quick Navigation
🎲 Probability of Two Events
To find out the union, intersection, and other related probabilities of two independent events.
Results
| Probability of A NOT occurring: P(A') | - | |
| Probability of B NOT occurring: P(B') | - | |
| Probability of A and B both occurring: P(A∩B) | - | |
| Probability that A or B or both occur: P(A∪B) | - | |
| Probability that A or B occurs but NOT both: P(A△B) | - | |
| Probability of neither A nor B occurring: P((A∪B)') | - | |
| Probability of A occurring but NOT B: | - | |
| Probability of B occurring but NOT A: | - |
🔍 Probability Solver for Two Events
Please provide any 2 values below to calculate the rest probabilities of two independent events.
Solver Results
📊 Probability of a Series of Independent Events
Series Results
📈 Probability of a Normal Distribution
Use the calculator below to find the area P shown in the normal distribution, as well as the confidence intervals for a range of confidence levels.
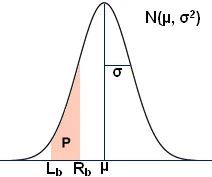
Normal Distribution Results
| Confidence | Range | n |
|---|
Understanding Probability
Basic Concepts
Probability is the measure of the likelihood of an event occurring. It is quantified as a number between 0 and 1, with 1 signifying certainty, and 0 signifying that the event cannot occur.
Complement: P(A') = 1 - P(A) represents the probability that event A does not occur.
Intersection: P(A ∩ B) represents the probability that both events A and B occur.
Union: P(A ∪ B) represents the probability that either event A or B (or both) occur.
Formulas
P(A ∪ B) = P(A) + P(B) - P(A ∩ B)
P(A ∩ B) = P(A) × P(B)
P(A ⊕ B) = P(A) + P(B) - 2 × P(A ∩ B)